CDC Director Believes US Has Reached Peak of RSV, While COVID-19 and Flu Cases Continue to Rise
As the United States continues to grapple with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, another respiratory virus has been causing concern among health officials. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), a common virus that typically affects young children, has seen an unexpected surge in cases across the country. However, there may be some relief on the horizon as the Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Dr. Rochelle Walensky, believes that the US has reached the peak of RSV infections.
RSV is a highly contagious virus that causes respiratory infections, primarily in infants and young children. It is responsible for millions of cases of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in children under the age of one every year. Typically, RSV infections occur during the winter months, but this year has seen an unusual increase in cases during the summer.
While RSV is not a new virus, the decrease in cases during the winter months due to COVID-19 restrictions may have contributed to a larger susceptible population. Additionally, the relaxation of preventive measures such as mask-wearing and social distancing as vaccination rates increased may have played a role in the recent surge.
The rise in RSV cases has put a strain on hospitals already overwhelmed by COVID-19 patients. Many hospitals have reported an increase in pediatric admissions due to RSV infections, leading to concerns about bed availability and resources. The combination of RSV, COVID-19, and the upcoming flu season has raised concerns about healthcare systems’ ability to handle the influx of patients.
However, there may be some positive news amidst these challenges. Dr. Walensky believes that the US has reached the peak of RSV infections and expects a decline in cases in the coming weeks. This prediction is based on historical trends and patterns observed with RSV outbreaks. As the summer months come to an end and children return to school, the spread of RSV is expected to decrease.
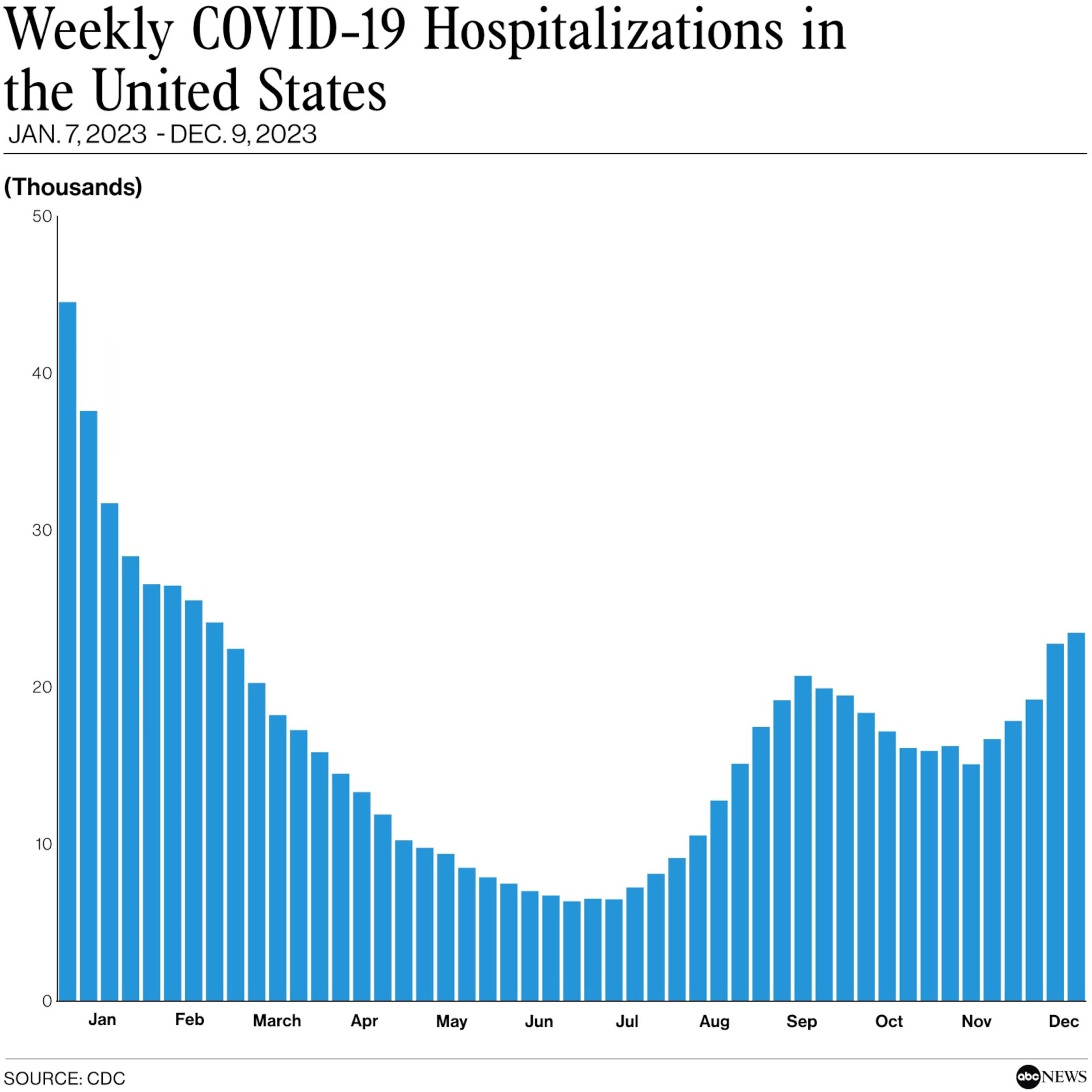
While the decline in RSV cases is encouraging, health officials are still grappling with the rise in COVID-19 and flu cases. The Delta variant of COVID-19 has been driving a surge in infections across the country, particularly among unvaccinated individuals. The highly transmissible nature of the Delta variant has led to breakthrough infections among vaccinated individuals as well.
To combat the rising cases, health officials continue to emphasize the importance of vaccination. COVID-19 vaccines have proven to be highly effective in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Vaccination not only protects individuals but also helps reduce the overall transmission of the virus in communities.
In addition to vaccination, preventive measures such as mask-wearing, social distancing, and hand hygiene remain crucial in reducing the spread of COVID-19 and other respiratory viruses. These measures have proven effective in controlling the spread of the virus and should be followed, especially in areas experiencing high transmission rates.
As the US faces the simultaneous challenges of RSV, COVID-19, and flu, it is essential for individuals to stay informed and take necessary precautions to protect themselves and others. Following public health guidelines, getting vaccinated, and practicing good hygiene can go a long way in mitigating the impact of these respiratory viruses on individuals and healthcare systems.