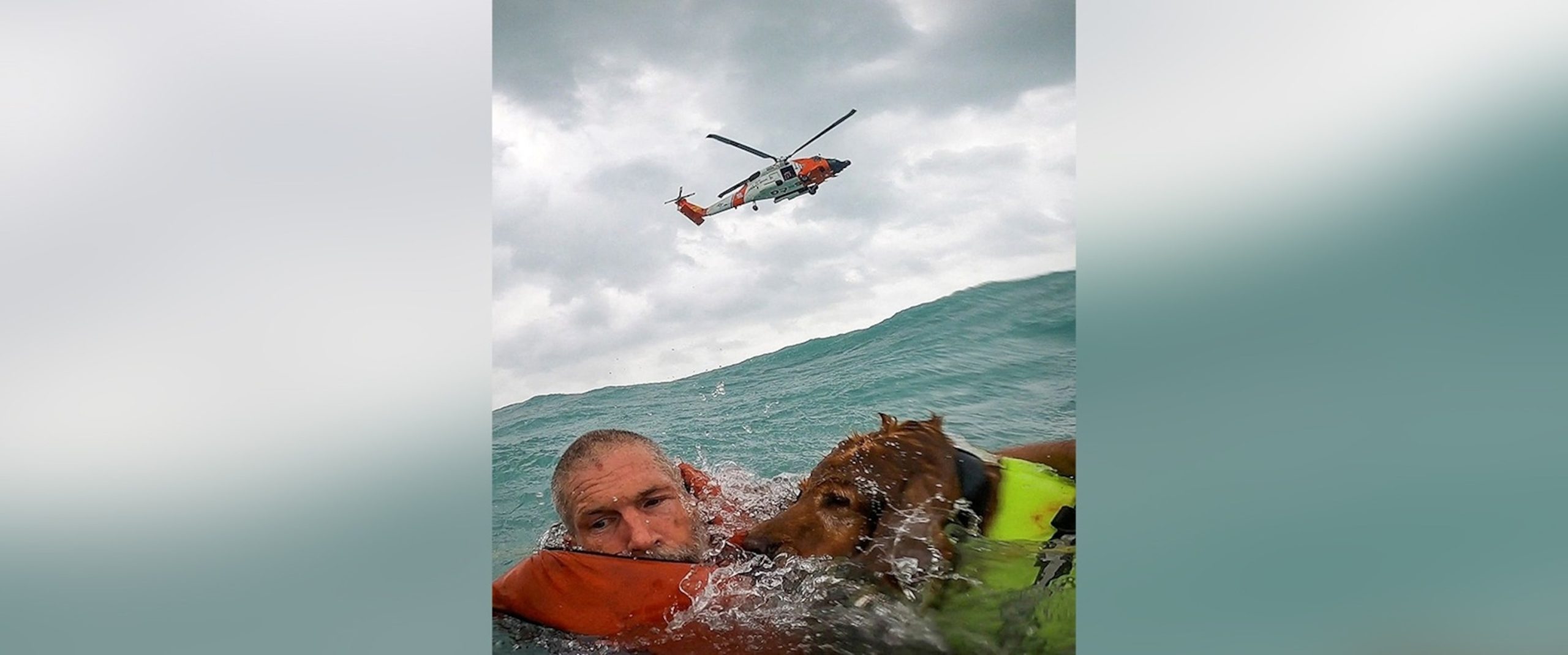
Hurricane Helene is heading straight for one of the regions most vulnerable to hurricanes: Florida’s Big Bend.
Helene is expected to make landfall as a dangerous major hurricane Thursday night near Tallahassee, marking another direct hit to the Big Bend. “Potentially catastrophic” wind and storm surge is possible in the region, where the Florida panhandle joins the southern-facing peninsula along the Gulf Coast, according to the National Hurricane Center.
The Big Bend, still reeling from Hurricane Idalia in 2022, is often in the bullseye of tropical storms forming in the Atlantic basin, experts told ABC News.
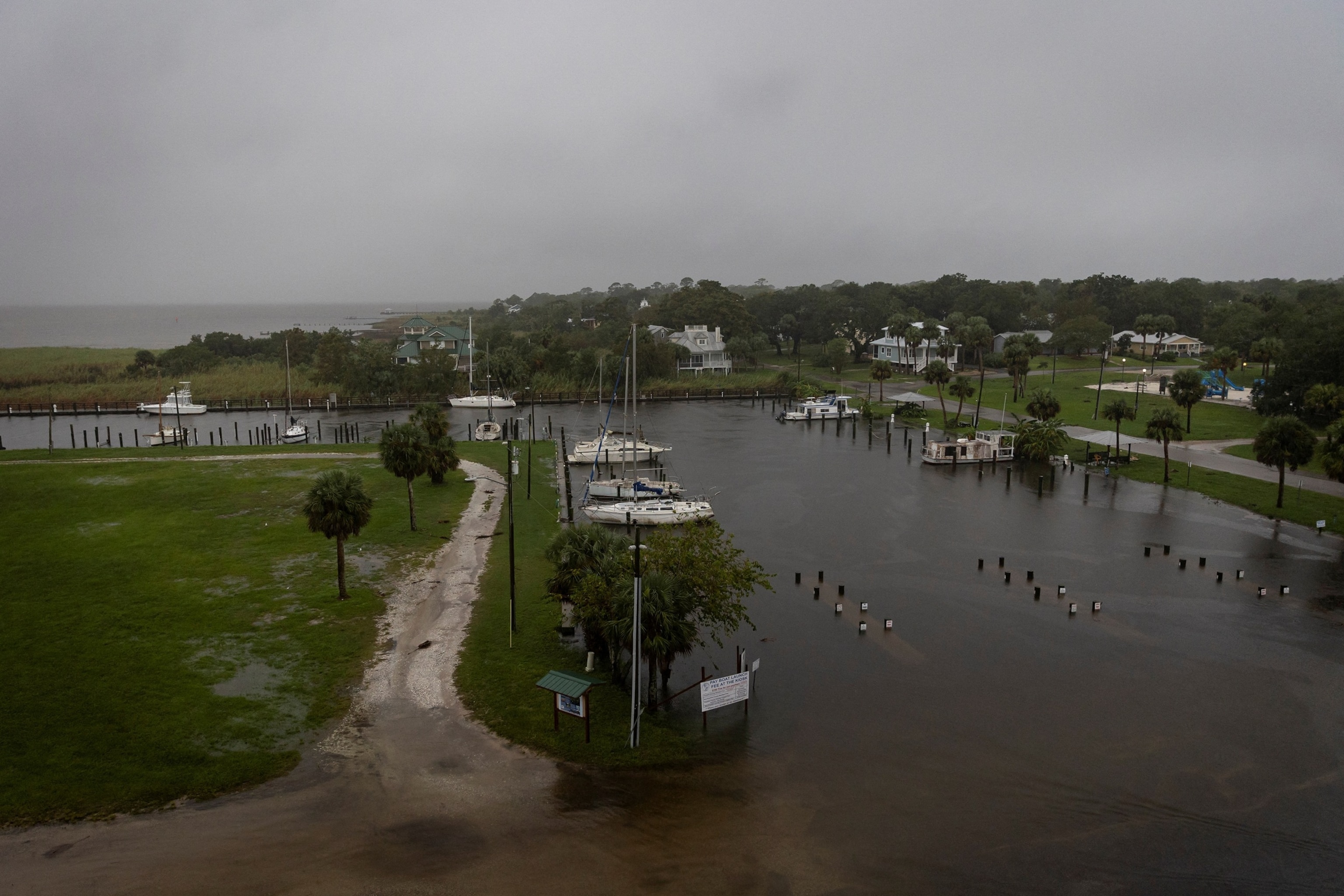

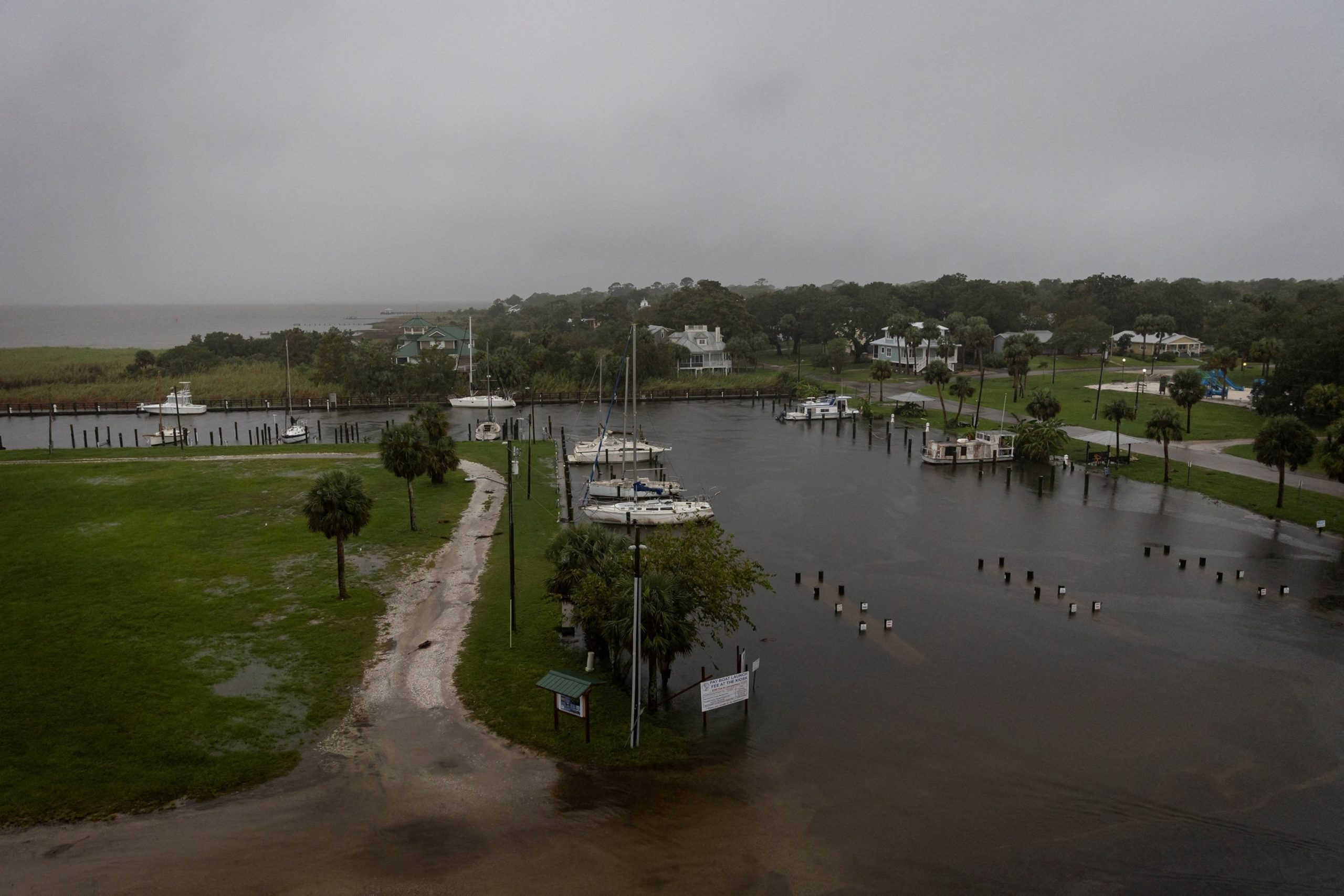
A view shows Battery Park as Hurricane Helene intensifies before its expected landfall on Florida’s Big Bend, in Apalachicola, Fla., Sept. 26, 2024.
Marco Bello/Reuters
Why Florida’s Big Bend is vulnerable to hurricanes
The Big Bend’s proximity to the Gulf of Mexico puts the region directly in line to be impacted from tropical storm activity.
“We’ve seen the Gulf Coast, generally, as the target for many of the storms over the last four or five years,” Marshall Shepherd, director of the Atmospheric Sciences Program at the University of Georgia and former president of the American Meteorological Society, told ABC News.
The underwater geology of the Gulf of Mexico leaves much of the low-lying coast unguarded against a massive influx of seawater. The continental shelf of the Florida Gulf Coast extends quite far offshore – up to 150 miles in some spots, according to the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – leaving the shallow waters nowhere to go.
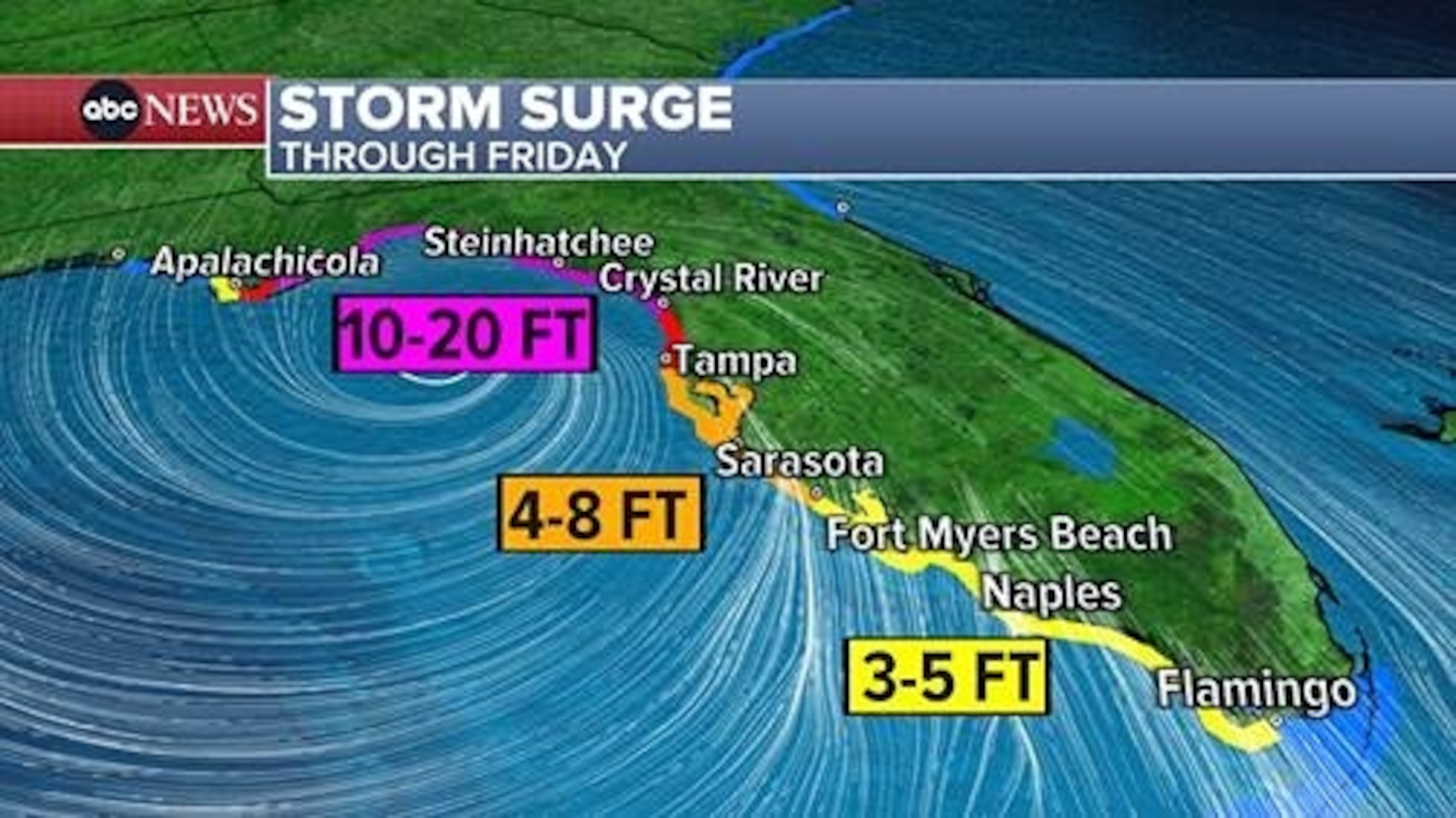
The sheer radius of Helene is going to make the storm surge particularly problematic, because the additional water gets “shoved” onto the coast for an extended amount of time, Shepherd said.
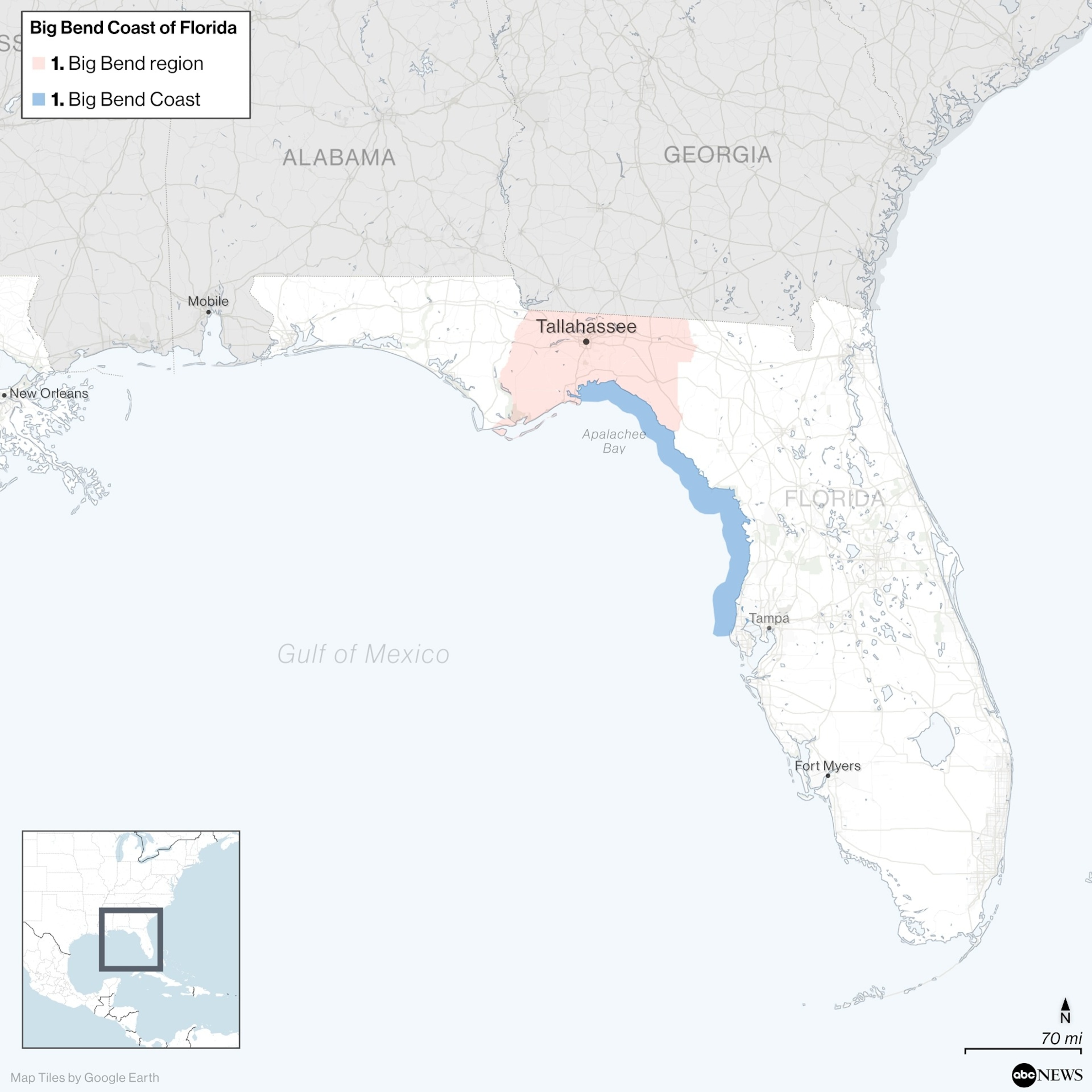
Big Bend coast of Florida
ABC News / Google Earth
Helene is forecast to bring a potentially life-threatening storm surge and dangerous coastal flooding along a wide swath of the Florida Gulf Coast. The storm surge is projected to rise to 20 feet high in the Big Bend area, forecasts show.
The Big Bend will also likely be hit by the eastern side of the storm, which typically carries the worst of the storm conditions and packs the strongest winds, Shepherd said.
“Stronger winds pile up more water, creating bigger storm surges,” Michael Mann, a professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Science at the University of Pennsylvania, told ABC News.
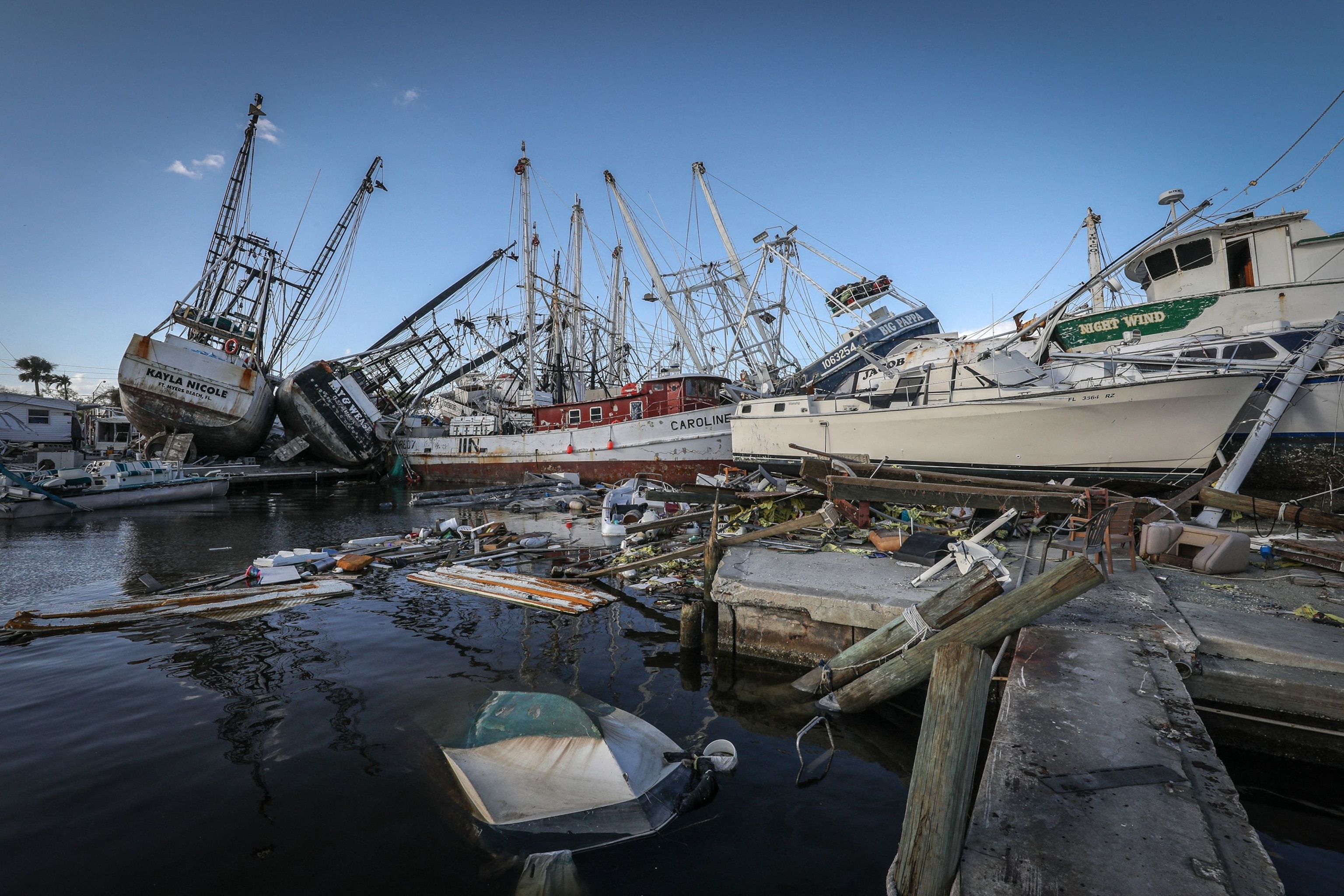

Piled up and destroyed boats are seen on San Carlos Island in Fort Myers Beach, Fla., after Hurricane Ian hit, Nov. 7, 2022.
Giorgio Viera/AFP via Getty Images
Steering currents in the Gulf of Mexico in recent years may also have been directing some storms on similar paths through Florida from the Gulf of Mexico, Shepherd said.
In addition, extensive loss of seagrass may be contributing to increased flooding following heavy rainfall and strong storms, scientists say. The northeastern Gulf of Mexico contains the second-largest contiguous seagrass meadow in the continental U.S. but had lost about 15% of its area between 2001 and 2022, according to a study published last year in the journal Environmental Management.
How climate change is exacerbating the situation
Human-caused climate change is the primary cause for present-day rising sea levels, according to a consensus of climate scientists. It’s also triggering more frequent and more intense extreme rainfall events, experts say.
While many factors contribute to the magnitude and impacts of storm surge and coastal flooding, average sea levels for many Gulf Coast communities are more than six inches higher today than they were just a few decades ago, data shows.
“We can’t talk about Hurricane Helene without talking about climate change, which is causing stronger and more destructive storms,” Mann said.
That sea level rise is also accelerating, research shows. Beginning in 2020, the overall U.S. coastline is projected to experience a sea level rise, on average, of about 11 inches through 2050, according to the federal government’s Fifth National Climate Assessment, a breakdown of the latest in climate science, published in November. That amount of sea level rise previously took 100 years to reach (between 1920 and 2020).
During that same time period, the eastern Gulf Coast is projected to experience an average sea level rise of 8 to 12 inches, with even greater increases of 12 to 16 inches along the western Gulf Coast.
In addition to the sea level rise, heavy rainfall on top of existing storm surge will increase Hurricane Helene’s coastal flooding impact along Florida’s Gulf Coast, experts say.
Warmer than average sea surface temperatures are also likely having an impact on the storm.
Helene’s path through the Northern Caribbean and Eastern Gulf of Mexico brought it across very warm ocean waters. Higher than normal sea surface temperatures in these regions were made at least 200 to 500 times more likely due to human-caused climate change, according to Climate Central’s Climate Shift Index. Warm ocean waters provide the energy hurricanes need to form and intensify.
However, while a link has been established between the usually warm sea surface temperatures and human-caused climate change, it is not yet known to what degree that climate change may have influenced Hurricane Helene’s development.

A man walks in the rain with bags of groceries as Hurricane Helene intensifies before its expected landfall on Florida’s Big Bend, in Apalachicola, Fla., Sept. 26, 2024.
Marco Bello/Reuters
Research suggests that hurricanes are now intensifying more quickly. Warmer than normal oceans hold a lot of extra energy that these storms can feed on, and about 80% of major hurricanes, between Categories 3 and 5, undergo rapid intensification, defined as an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of about 35 mph or more in a 24-hour period.
Observational improvements and the natural variability of tropical cyclones, especially in the Atlantic Basin, in recent decades also play a role in the observed increase of rapid intensification events, according to NOAA. Hurricane Helene has fed on record levels of upper ocean heat content in the Gulf, favoring very rapid intensification, Mann said.
“Helene is a poster-child for the ways that human-caused climate change is amplifying the coastal threat from intensified hurricanes combined with rising sea levels,” he added.
ABC News’ Matthew Glasser and Daniel Peck contributed to this report.
The Big Bend region of Florida, known for its picturesque coastline and diverse ecosystems, is facing increased vulnerability to tropical threats due to the impacts of climate change. One recent example of this is Hurricane Helene, which made landfall in the region with devastating consequences.
Climate change has been linked to the increase in the intensity and frequency of tropical storms and hurricanes. Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for these storms to form and strengthen, leading to more destructive impacts when they make landfall. The Big Bend region, with its low-lying coastal areas and abundant wetlands, is particularly susceptible to the effects of these powerful storms.
Hurricane Helene, a Category 3 storm, brought heavy rainfall, strong winds, and storm surge to the Big Bend region, causing widespread flooding and damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure. The storm also had a significant impact on the region’s natural habitats, with reports of coastal erosion and damage to sensitive ecosystems.
In addition to the immediate impacts of Hurricane Helene, the storm also highlighted the long-term vulnerabilities of the Big Bend region to future tropical threats. Rising sea levels, another consequence of climate change, are exacerbating the risk of coastal flooding and erosion in the area. This poses a serious threat to communities along the coast and puts pressure on local governments to invest in infrastructure improvements and adaptation measures.
The Big Bend region is also home to a number of important industries, including tourism, fishing, and agriculture, which are all at risk from the impacts of climate change. The destruction caused by Hurricane Helene serves as a stark reminder of the need for proactive measures to protect these vital sectors from future storms and other climate-related threats.
In response to the increasing vulnerability of the Big Bend region to tropical threats like Hurricane Helene, local authorities and residents are taking steps to improve preparedness and resilience. This includes investing in early warning systems, strengthening building codes, and promoting sustainable land use practices to reduce the risk of damage from future storms.
Ultimately, the impact of climate change on Florida’s Big Bend region is clear: increased vulnerability to tropical threats like Hurricane Helene. As the frequency and intensity of these storms continue to rise, it is essential for communities in the region to work together to adapt and mitigate the risks posed by a changing climate. By taking proactive steps now, we can help protect the natural beauty and economic vitality of this unique and vulnerable region for generations to come.



