California Gov. Gavin Newsom dealt a blow to legislation linked to the state’s groundbreaking reparations efforts on Wednesday.
He vetoed Senate Bill 1050, which would have restored property taken under racially-motivated uses of eminent domain to its original owners or provide another remedy, such as restitution or compensation.
“I thank the author for his commitment to redressing past racial injustices,” Newsom said in a statement, referring to state Sen. Steven Bradford. “However, this bill tasks a nonexistent state agency to carry out its various provisions and requirements, making it impossible to implement.”

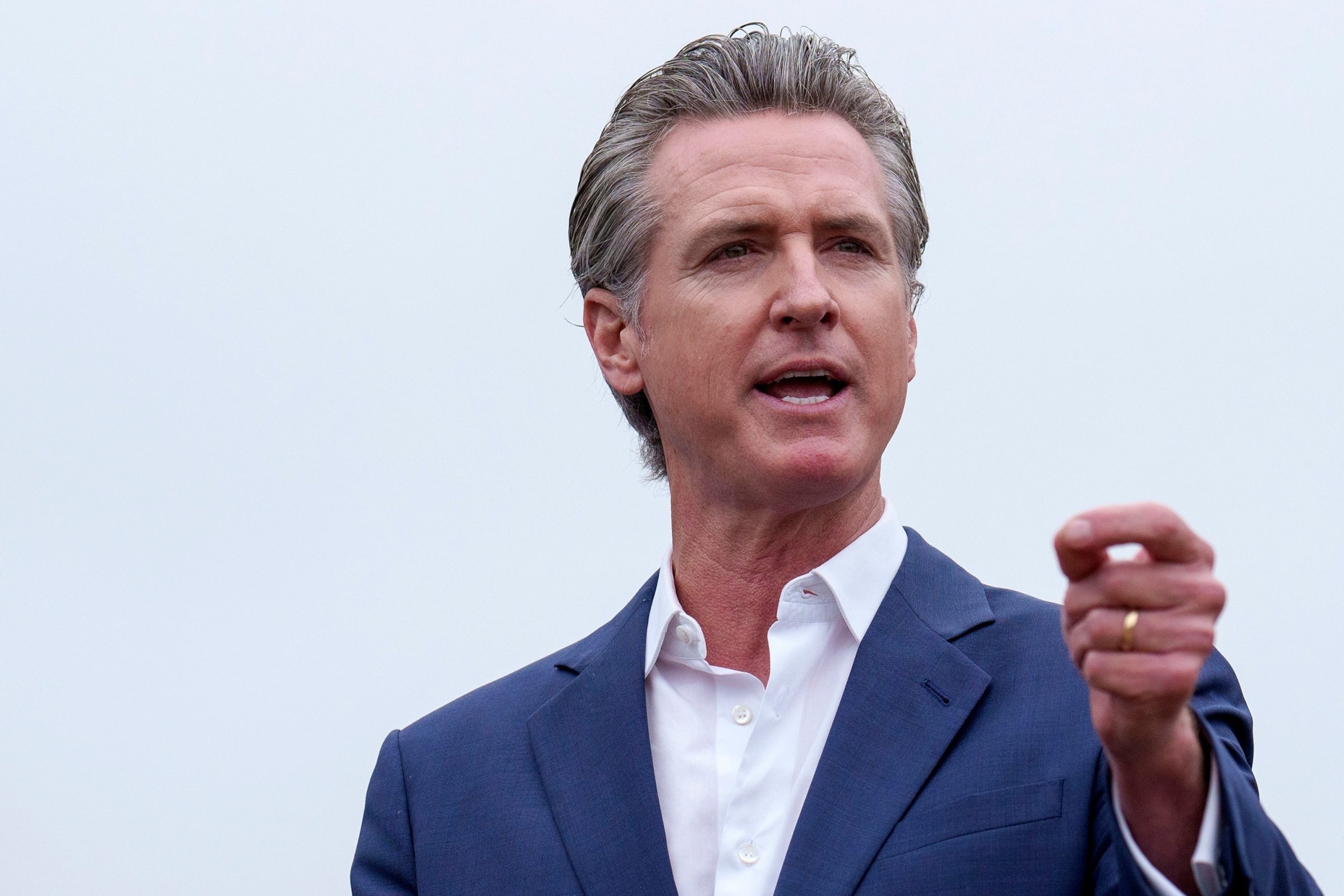
California Gov. Gavin Newsom speaks during a press conference in Los Angeles, on Sept. 25, 2024.
Eric Thayer/AP
The agency that would have carried out the policy would have been created if Senate Bill 1403 passed the legislature. The bill, also introduced by Bradford, was intended to create an agency to carry out the recommendations of the state’s groundbreaking first-in-the-nation Task Force to Study and Develop Reparation Proposals for African Americans.
It failed following last-minute changes from the Newsom administration that instead aimed to to support further research on reparations in the state instead of creating the agency to carry out reparations recommendations from the state task force, according to local news outlet CalMatters.
Newsom signed Assembly Bill 3131, which requires the state department of education to prioritize funding for socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, on Sept. 22.
This bill would require the department, in consultation with the executive director of the State Board of Education, when determining grant recipients for the California Career Technical Education Incentive Grant Program, to first give priority consideration to applicants in historically redlined communities, as determined by the department. The same would apply to the K–12 Selection Committees, when determining grant recipients under the K–12 component of the Strong Workforce Program.
Several other bills from a legislative reparations package from the California Legislative Black Caucus are awaiting a response from Newsom. The package aimed to capture the many forms that reparations can take, according to Assemblywoman Lori D. Wilson, chair of the California Legislative Black Caucus.
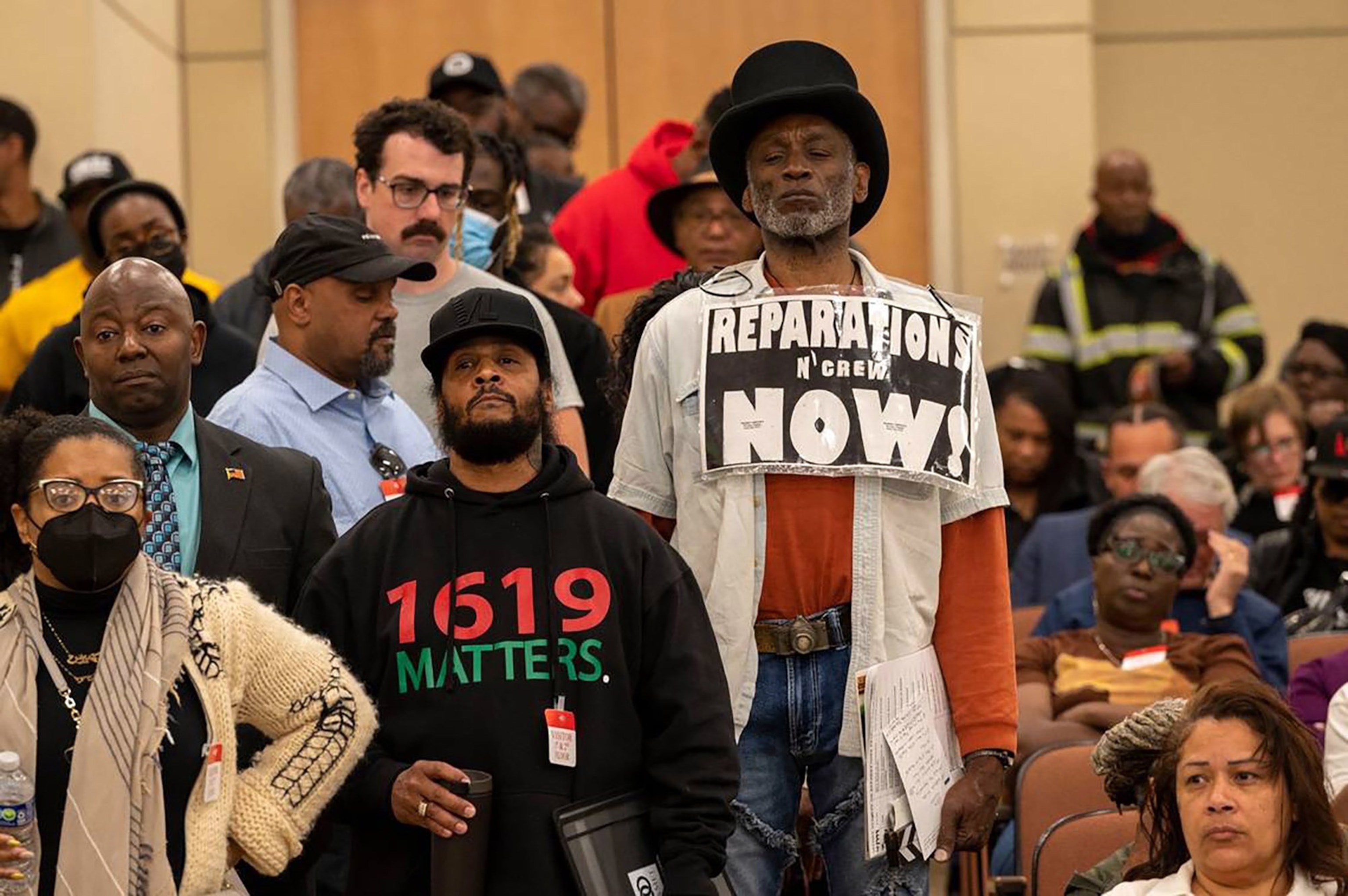
Morris Griffin, wearing a sign that says “reparations now,” waits in a line to speak during public comment in 2023 at a meeting of the California Reparations Task Force, which convened for a second day at the California Environmental Protection Agency in Sacramento, California.
Lezlie Sterling/The Sacramento Bee via TSN via Newscom, FILE
“While many only associate direct cash payments with reparations, the true meaning of the word, to repair, involves much more,” said Wilson in the introduction of the legislative package.
She noted that the package addressed the need for “a comprehensive approach to dismantling the legacy of slavery and systemic racism.”
This legislative package was born out of California’s first-in-the-nation state-backed task force that found the state and various arms of its government played an active role in perpetuating systemic racism against Black Californians through discrimination in housing, education and employment.
The bills that await a response from Newsom include Assembly Bill 3089, which would issue a formal apology from the state of California for “all of the harms and atrocities committed by the state” for perpetuating racial discrimination through chattel slavery, segregation, unequal disbursal of government funding and more.

In this Oct. 13, 2012, file photo, Pelican Bay State Prison inmates stand in the yard as they move from one spot to another during an exercise period in Crescent City, Calif.
Mark Boster/Los Angeles Times via Getty Images, FILE
This bill “declares that such actions shall not be repeated” and “commits to restore and repair affected peoples with actions beyond this apology.”
Senate Bill 1089 would address food and health inequities by requiring advance notification if a grocery store or pharmacy is closing in an underserved or at-risk community.
The other 10 bills from the California Legislative Black Caucus’ 14-bill reparations package failed to make it through the legislature.
The bills that failed to make it through the legislature included bans on involuntary servitude and solitary confinement in state detention facilities, funding for violence reduction programs, and funding “for the purpose of increasing the life expectancy of, improving educational outcomes for, or lifting out of poverty specific groups.”
Governor Gavin Newsom’s recent decision to sign a bill establishing a task force to study and develop proposals for reparations for African Americans in California has sparked both excitement and controversy. The bill, AB 3121, was introduced by Assemblymember Shirley Weber and passed by the state legislature in September.
The task force will be made up of nine members, with five appointed by the governor and four appointed by the state legislature. The group will be tasked with studying the impact of slavery on African Americans in California and developing proposals for reparations, which could include financial compensation, community investments, and other forms of redress.
Newsom’s decision to sign the bill has been hailed as a step forward in addressing the legacy of slavery and systemic racism in California. Supporters of reparations argue that African Americans have long been denied equal opportunities and access to resources due to historical injustices, and that reparations are a necessary step towards achieving racial equity.
However, there are also critics of the bill who argue that reparations are not the answer to addressing racial disparities in California. Some opponents believe that reparations would be too costly and impractical to implement, while others argue that they would be divisive and could lead to backlash from other marginalized groups.
Despite the controversy surrounding the issue, Newsom’s decision to establish a task force on reparations is a significant development in the ongoing efforts to address racial inequality in California. The task force will have a year to study the issue and develop recommendations, which will then be presented to the governor and legislature for consideration.
Overall, Governor Newsom’s decision to support reparations efforts in California reflects a growing recognition of the need to address historical injustices and systemic racism in the state. While there are differing opinions on the best approach to reparations, the establishment of a task force is a positive step towards achieving greater racial equity and justice for African Americans in California.



