NEW YORK — Some people should consider taking an antibiotic as a morning-after pill to try to prevent certain sexually transmitted diseases, U.S. health officials recommended Tuesday.
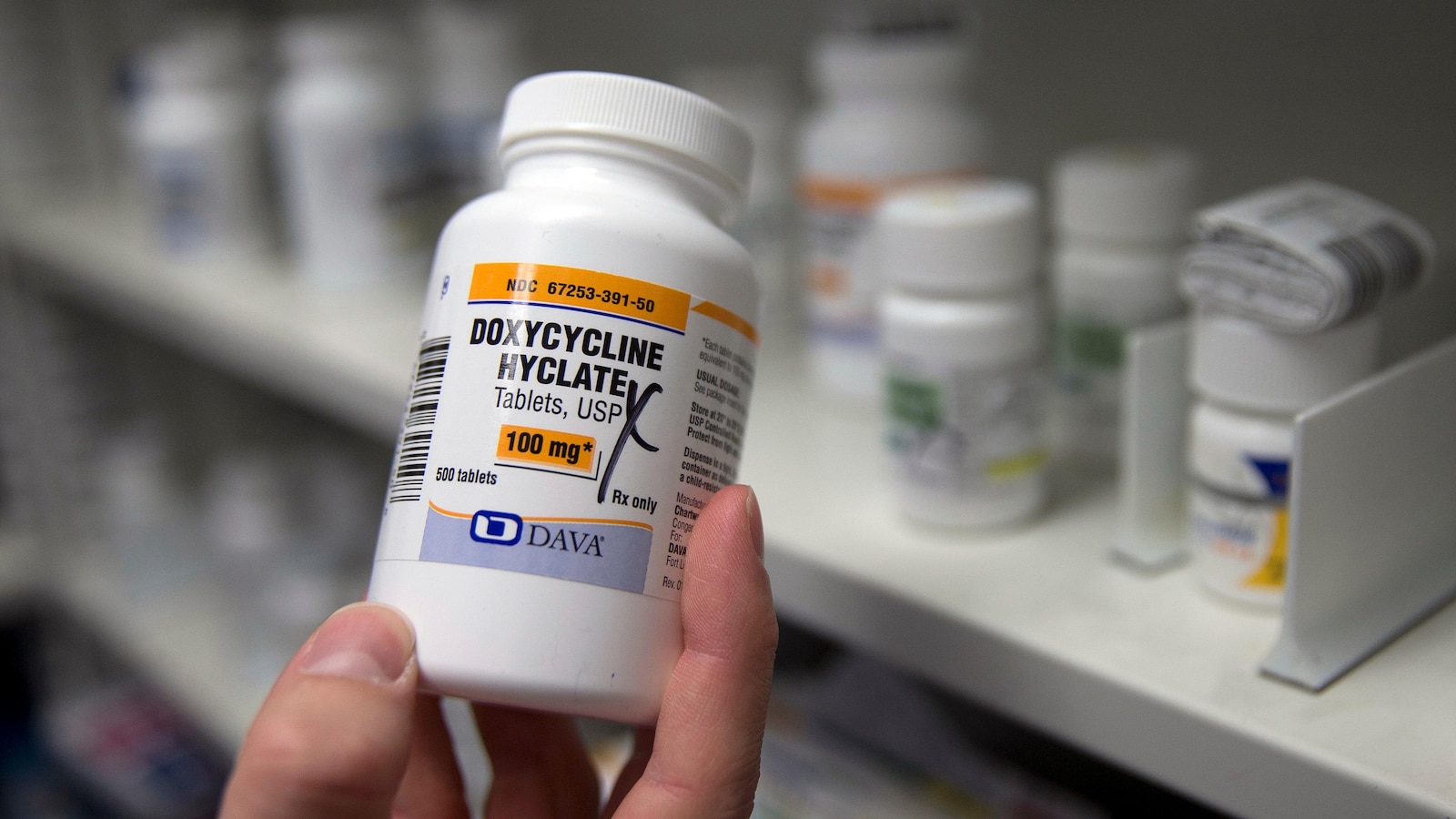
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention finalized its endorsement of taking doxycycline after unprotected sex as a way to prevent chlamydia, gonorrhea or syphilis infections.
CDC officials called it the first new prevention tool against sexually transmitted infections in decades, and said innovation is badly needed. Rates of syphilis, chlamydia and gonorrhea have been rising for years, most notably in gay and bisexual men, although the latest data suggested chlamydia and gonorrhea cases stopped rising in 2022.
The new guideline is specific to gay and bisexual men and transgender women who had an STD in the previous year and are at high risk of getting infected again. Studies have demonstrated doxycycline works in that group, but there’s not sufficient evidence to make the same recommendation for other people, agency officials said.
Officials call the treatment doxy PEP, short for doxycycline postexposure prophylaxis. Doctors can write a prescription for one dose of 200 milligrams of doxycycline to be taken within three days of unprotected sex, the CDC said.
In October, the CDC released a draft version of the guidelines. The proposed language was changed somewhat after a public comment period. Changes include clarifying language that the pills should be taken only once per 24 hours, and that doctors should reassess the regimen with patients every three to six months.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) continue to be a major public health concern, with millions of new cases reported each year. In an effort to combat the spread of these infections, health officials are now recommending the use of antibiotics as a preventative measure.
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, including many STDs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. However, recent research has shown that antibiotics can also be effective in preventing these infections from occurring in the first place.
One study published in the journal Sexually Transmitted Infections found that taking a single dose of the antibiotic doxycycline after unprotected sex reduced the risk of developing chlamydia by up to 50%. This is significant, as chlamydia is one of the most common STDs in the United States, with over 1.7 million cases reported each year.
Similarly, another study published in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases found that taking a daily dose of the antibiotic azithromycin reduced the risk of contracting gonorrhea by up to 70%. Gonorrhea is another common STD, with over 500,000 cases reported each year.
These findings have led health officials to recommend the use of antibiotics as a preventative measure against STDs, particularly for individuals who are at high risk of infection. This includes people who have multiple sexual partners, engage in unprotected sex, or have a history of STDs.
It is important to note that antibiotics should not be used as a substitute for safe sex practices, such as using condoms and getting regular STD screenings. However, for individuals who are at high risk of infection, taking antibiotics as a preventative measure can provide an additional layer of protection.
It is also important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any antibiotic regimen, as they can help determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects of antibiotics, which can include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions.
In conclusion, the use of antibiotics as a preventative measure against STDs is a promising new approach in the fight against these infections. By combining antibiotics with safe sex practices and regular screenings, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting STDs and help protect their overall health.