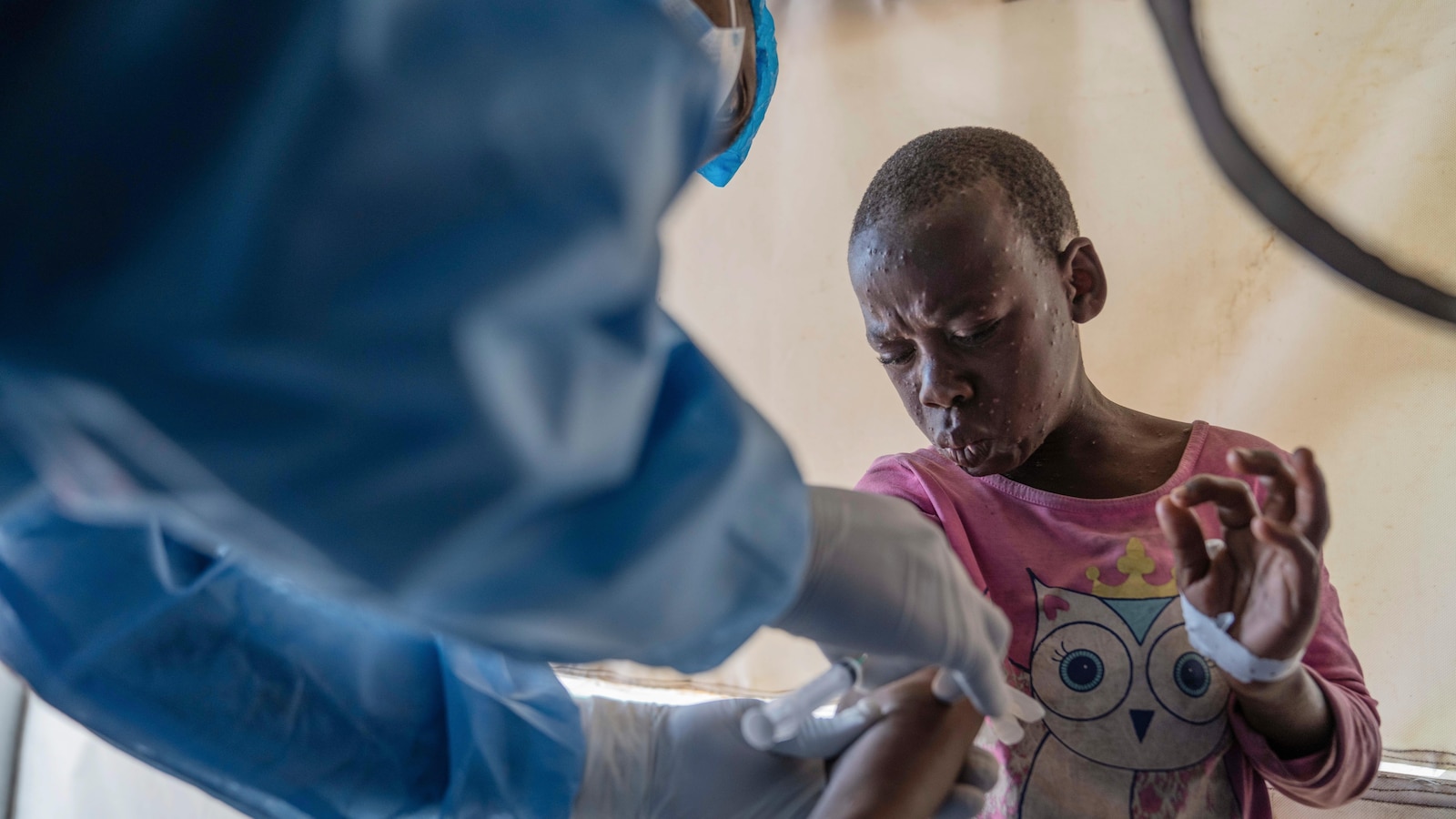
GENEVA — The World Health Organization said Friday it has granted its first authorization for use of a vaccine against mpox in adults, calling it an important step toward fighting the disease in Africa.
The approval of the vaccine by Bavarian Nordic A/S means that donors like vaccines alliance Gavi and UNICEF can buy it. But supplies are limited because there’s only a single manufacturer.
“This first (authorization) of a vaccine against mpox is an important step in our fight against the disease, both in the context of the current outbreaks in Africa, and in future,” said WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus.
The U.N. health agency chief called for “urgent” scale-up of procurement, donations and rollout to get the vaccine where it is needed most, along with other response measures.
Under the WHO authorization, the vaccine can be administered in people aged 18 or above in a two-dose regimen. The approval says that while the vaccine is not currently licensed for those under 18 years old, it may be used in infants, children and adolescents “in outbreak settings where the benefits of vaccination outweigh the potential risks.”
The mpox vaccine made by Bavarian Nordic was previously authorized by numerous rich countries across Europe and North America during the global mpox outbreak in 2022. Millions of doses given to adults showed the vaccine helped slow the virus’ spread, but there is limited evidence of how it works in children.
Officials at the Africa Center for Disease Control and Prevention said last month that nearly 70% of cases in Congo — the country hardest hit by mpox — are in children younger than 15, who also accounted for 85% of deaths.
Overall, WHO said over 120 countries have confirmed more than 103,000 cases of mpox since the outbreak began two years ago. Its latest tally, as of Sunday, showed that 723 people in more than a dozen countries in Africa have died of the disease.
African experts have estimated they might need about 10 million vaccines to stop the ongoing outbreaks on the continent. As of last week, Congo, the most-affected country, had received only about 250,000 doses.
On Thursday, the Africa CDC said 107 new deaths and 3,160 new cases had been recorded in the past week, just a week after it and WHO launched a continental response plan.
Mpox belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox but causes milder symptoms like fever, chills and body aches. People with more serious cases can develop lesions on the face, hands, chest and genitals.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently approved the first ever MPOX vaccine, marking a significant milestone in the global fight against infectious diseases. MPOX, short for Multi-Pathogen Oxidative Xenoantigen, is a novel vaccine technology that has shown promising results in enhancing the body’s immune response to a wide range of pathogens.
The development of the MPOX vaccine comes at a critical time when the world is facing increasing challenges from emerging infectious diseases such as COVID-19, Ebola, and Zika. Traditional vaccines typically target a single pathogen, making it difficult to respond effectively to outbreaks of multiple diseases simultaneously. The MPOX vaccine, on the other hand, is designed to stimulate a broad immune response against a variety of pathogens, providing a more comprehensive defense against infectious diseases.
One of the key advantages of the MPOX vaccine is its ability to activate the body’s oxidative stress response, which plays a crucial role in fighting off infections. By targeting this pathway, the vaccine can boost the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy a wide range of pathogens, offering a more robust and versatile defense mechanism.
The approval of the MPOX vaccine by the WHO represents a major breakthrough in vaccine technology and holds great promise for improving disease response efforts around the world. With its ability to enhance the body’s immune response to multiple pathogens, the MPOX vaccine has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach infectious disease prevention and control.
In addition to its broad-spectrum protection, the MPOX vaccine also offers several other benefits, including increased durability of immune response, reduced risk of vaccine resistance, and improved vaccine efficacy in vulnerable populations. These features make the MPOX vaccine an invaluable tool in the fight against infectious diseases, particularly in regions where access to healthcare resources is limited.
As countries continue to grapple with the challenges of emerging infectious diseases, the approval of the MPOX vaccine by the WHO represents a significant step forward in strengthening global disease response efforts. By harnessing the power of innovative vaccine technologies like MPOX, we can better prepare ourselves to combat the threats posed by infectious diseases and protect the health and well-being of populations worldwide.


