An Overview of Nepal’s Most Devastating Earthquakes
Nepal, a small landlocked country located in the Himalayas, is no stranger to earthquakes. Situated on the boundary of two tectonic plates, the Indian and Eurasian plates, Nepal experiences frequent seismic activity. Over the years, the country has witnessed several devastating earthquakes that have left a lasting impact on its people and infrastructure. This article provides an overview of Nepal’s most devastating earthquakes.
1. The Great Nepal-Bihar Earthquake (1934):
One of the deadliest earthquakes in Nepal’s history occurred on January 15, 1934. Known as the Great Nepal-Bihar Earthquake, it had a magnitude of 8.0 and caused widespread destruction in both Nepal and the neighboring Indian state of Bihar. The earthquake claimed approximately 10,000 lives in Nepal and around 8,500 lives in Bihar. Many historical buildings and temples were reduced to rubble, including the iconic Dharahara Tower in Kathmandu.
2. The Nepal-India Earthquake (1988):
On August 21, 1988, Nepal was struck by a powerful earthquake with a magnitude of 6.8. The epicenter was located near the eastern border between Nepal and India. This earthquake caused significant damage to infrastructure and claimed the lives of around 1,000 people. The town of Damak in eastern Nepal was particularly affected, with many buildings collapsing and landslides occurring in the surrounding areas.
3. The Gorkha Earthquake (2015):
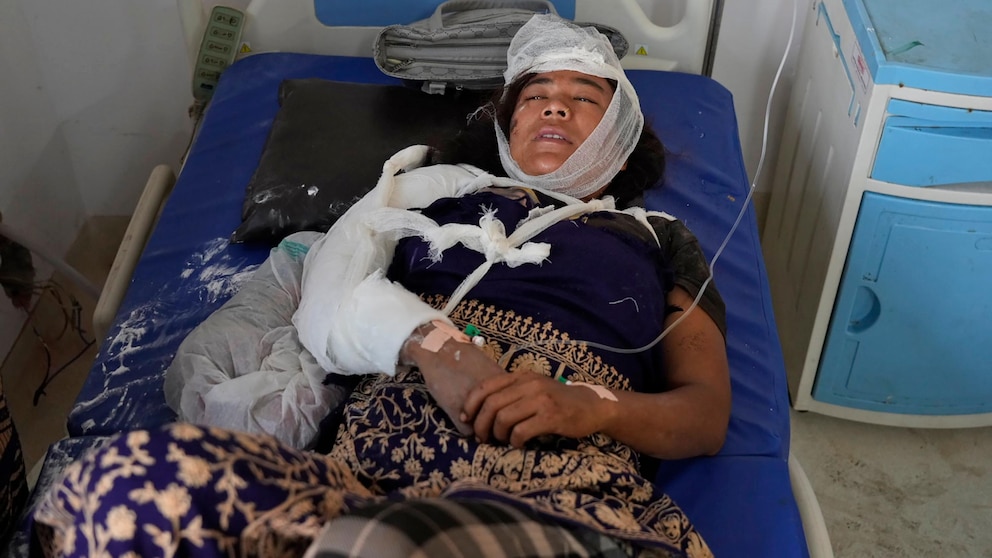
The most devastating earthquake in recent history struck Nepal on April 25, 2015. Known as the Gorkha Earthquake or the Nepal Earthquake, it had a magnitude of 7.8. The epicenter was located in Gorkha district, approximately 80 kilometers northwest of Kathmandu. This earthquake caused widespread destruction across the country, resulting in the loss of over 8,000 lives and injuring more than 22,000 people.
The Gorkha Earthquake triggered numerous landslides and avalanches, damaging infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and historical monuments. The iconic Dharahara Tower, which had been rebuilt after the 1934 earthquake, once again collapsed. The earthquake also caused severe damage to cultural heritage sites such as the Kathmandu Durbar Square, Bhaktapur Durbar Square, and Patan Durbar Square, all of which are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
The international community rallied to provide aid and support to Nepal in the aftermath of the Gorkha Earthquake. Rescue teams from various countries arrived to assist in search and rescue operations, while humanitarian organizations provided emergency relief supplies and medical assistance. The Nepalese government, with the help of international partners, initiated a massive reconstruction effort to rebuild the affected areas and strengthen infrastructure against future earthquakes.
In conclusion, Nepal has experienced several devastating earthquakes throughout its history. The Great Nepal-Bihar Earthquake in 1934, the Nepal-India Earthquake in 1988, and the Gorkha Earthquake in 2015 have all left a lasting impact on the country. These earthquakes have claimed thousands of lives and caused significant damage to infrastructure and cultural heritage sites. However, Nepal has shown resilience in the face of adversity, with efforts focused on reconstruction and building a more resilient nation capable of withstanding future seismic events.