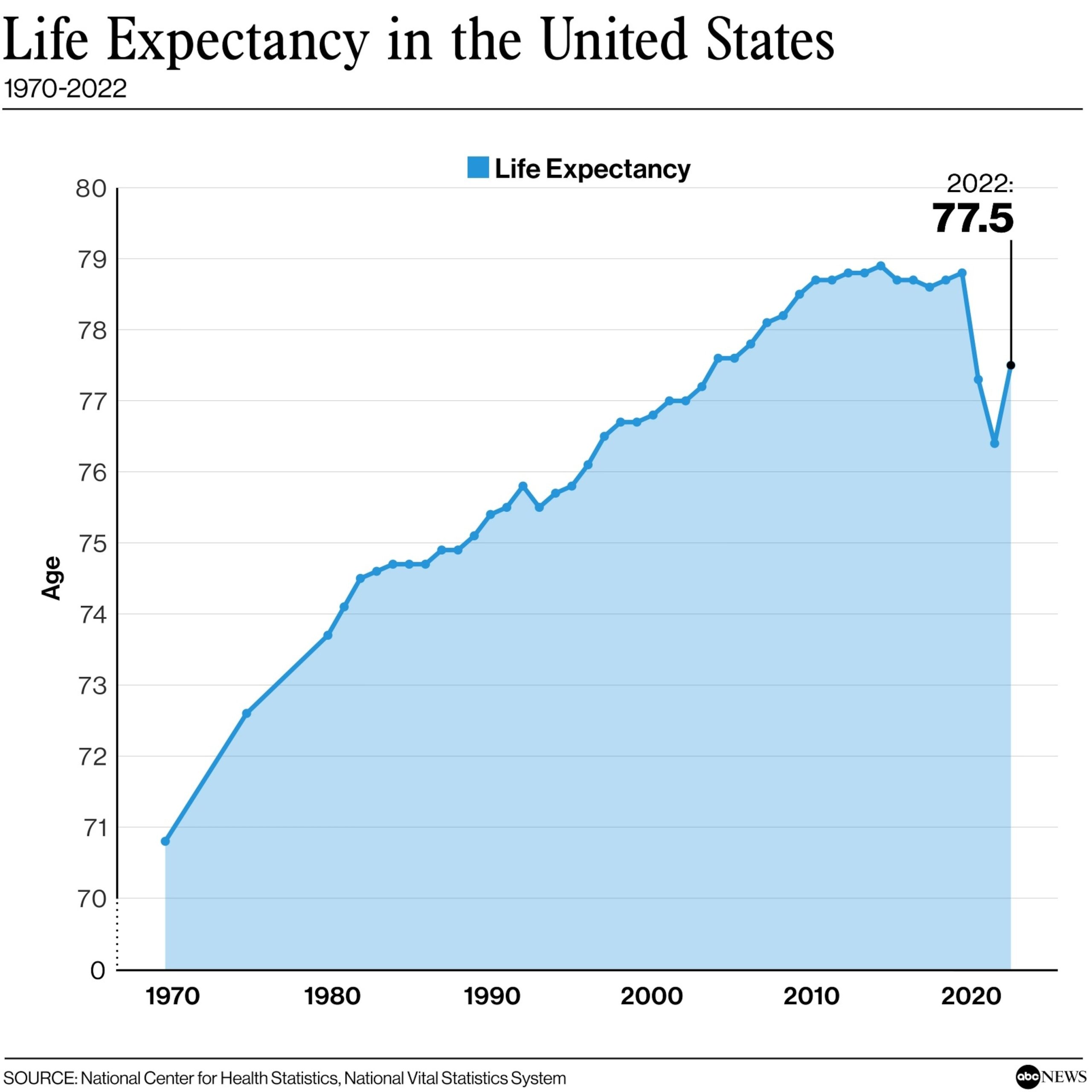
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recently reported a significant decrease in cases of both influenza (flu) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) compared to the previous year. This news comes as a relief to many, considering the devastating impact these viruses have had on public health in the past.
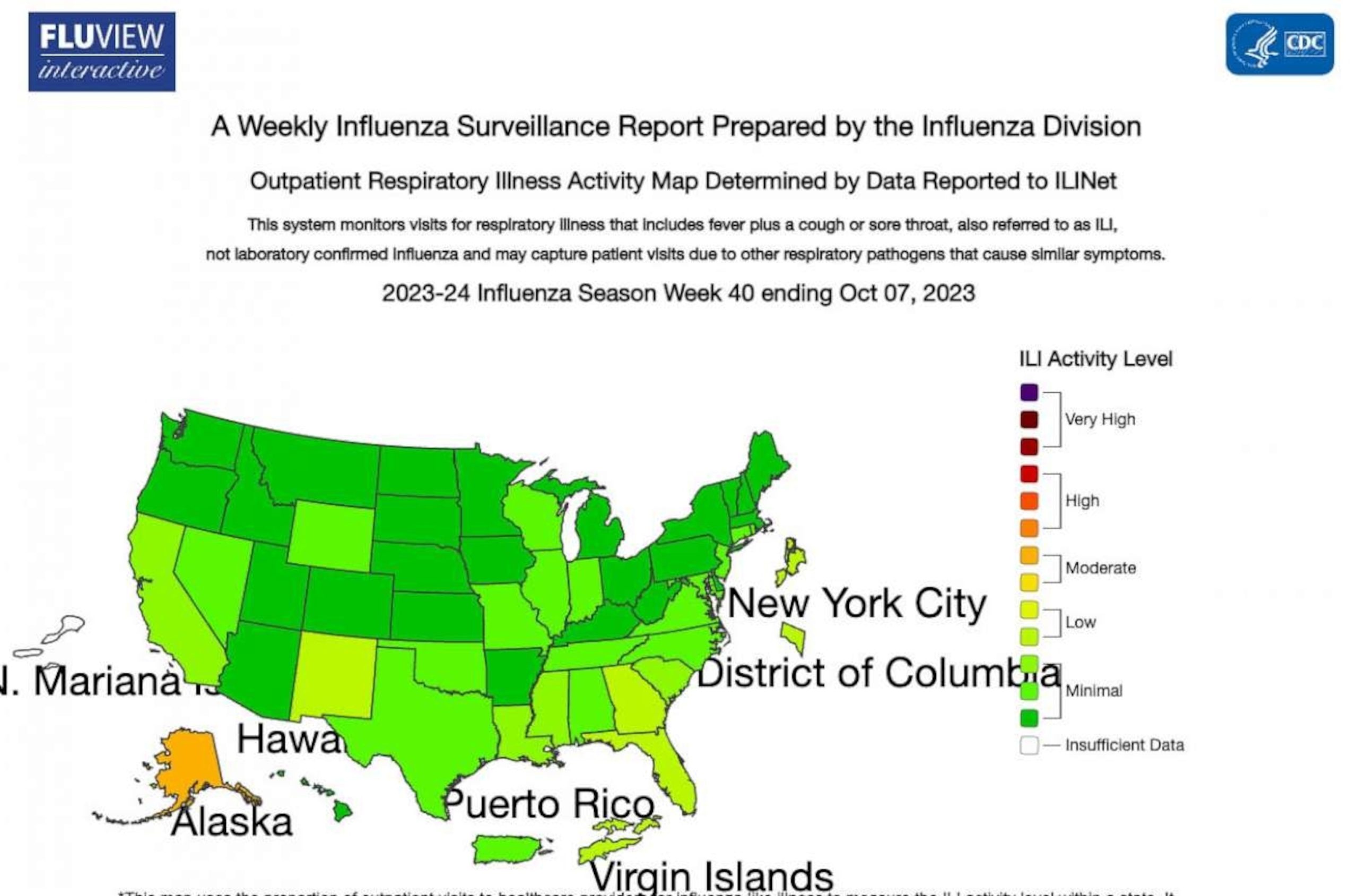
The CDC’s latest surveillance data reveals that flu activity during the 2020-2021 season was remarkably low compared to previous years. The number of reported cases, hospitalizations, and deaths related to the flu were significantly lower than historical averages. This decline can be attributed to various factors, including increased adherence to preventive measures such as mask-wearing, social distancing, and improved hygiene practices.
The COVID-19 pandemic, which led to widespread adoption of these preventive measures, likely played a crucial role in reducing flu transmission. The same precautions that help prevent the spread of COVID-19, such as wearing masks and frequent handwashing, are also effective in preventing the flu. Additionally, the development and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines may have indirectly contributed to lower flu cases by promoting overall awareness and acceptance of vaccination.
In addition to the decline in flu cases, the CDC also reported a significant reduction in RSV circulation. RSV is a common respiratory virus that can cause severe illness, particularly in young children and older adults. Typically, RSV infections peak during the winter months, leading to increased hospitalizations and emergency room visits. However, during the 2020-2021 season, RSV activity remained unusually low.
Similar to the decline in flu cases, the decreased circulation of RSV can be attributed to the preventive measures implemented to combat COVID-19. The reduced social interactions, increased hand hygiene, and limited travel likely contributed to the decline in RSV transmission. Additionally, school closures and remote learning may have played a role in reducing RSV outbreaks among children.
While the decline in flu and RSV cases is undoubtedly positive news, it is important to remain vigilant. As COVID-19 restrictions ease and people resume normal activities, there is a possibility of increased transmission of these respiratory viruses. The CDC continues to emphasize the importance of vaccination against the flu and adherence to preventive measures to minimize the risk of infection.
Furthermore, the CDC advises healthcare providers to remain vigilant for any potential resurgence of flu and RSV cases. Timely diagnosis, surveillance, and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing these respiratory illnesses, especially in vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, the CDC’s recent report on lower cases of flu and RSV circulation compared to last year brings hope and relief amidst the ongoing pandemic. The decline can be attributed to the widespread adoption of preventive measures and increased vaccination efforts. However, it is essential to maintain these practices to prevent future outbreaks and protect public health.