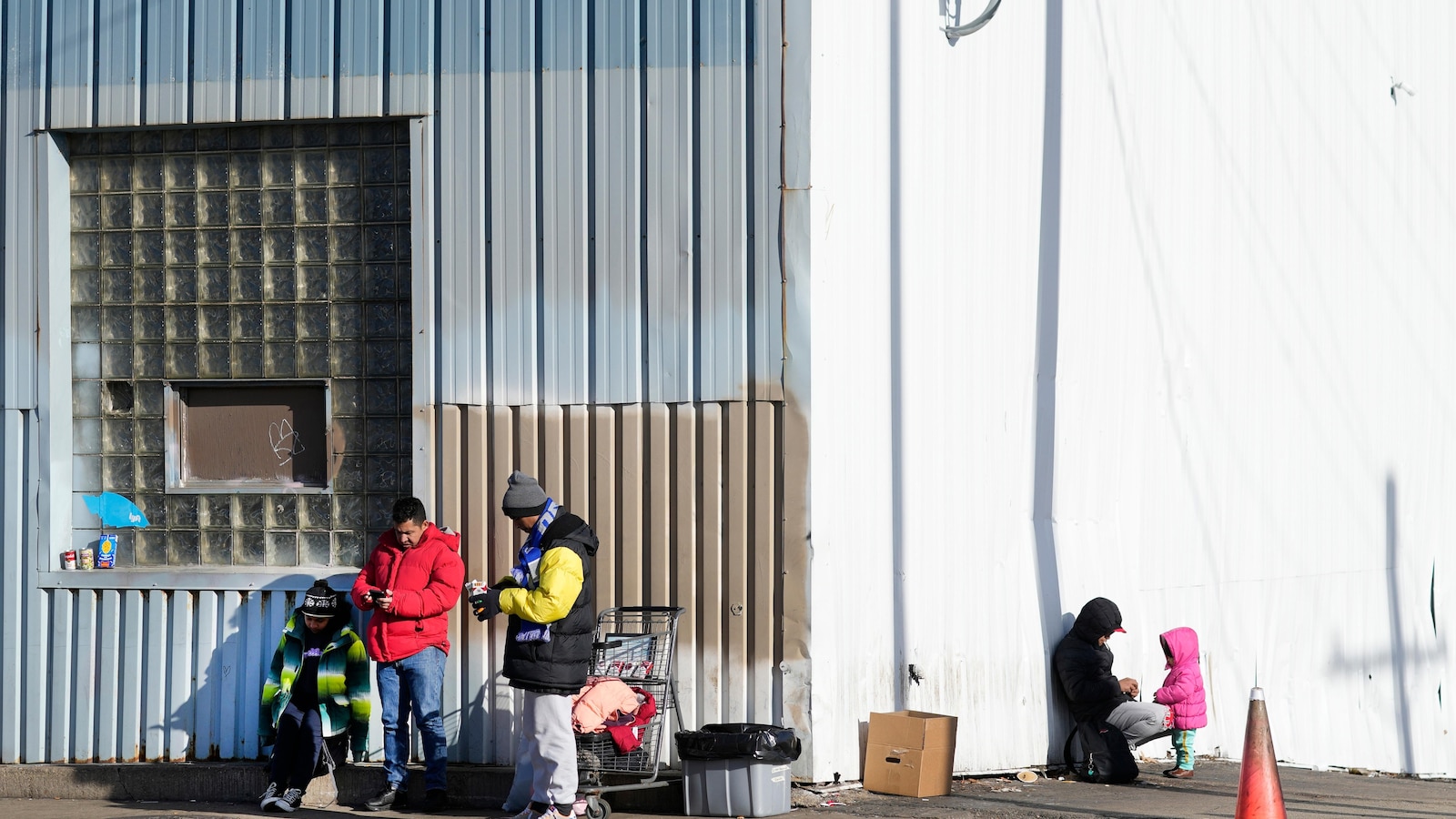
CHICAGO — Seven people living at a Chicago shelter for migrants have tested positive for measles since last week, prompting the arrival of a team with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to guide city and state officials’ response to the infections, including vaccination efforts.
Eight infections total have been reported in the city since Thursday, which the Chicago Department of Public Health said was the first instance of measles detected locally since 2019. The first case — an adult — was not a shelter resident.
Measles is a contagious virus still common in many countries outside the U.S. Cases in the U.S. originate from international travelers — most often Americans who have not been vaccinated, according to the CDC.
The city on Friday publicly reported the first case at the shelter housing around 1,900 people. The other cases at the former warehouse in the city’s Pilsen neighborhood quickly followed, including three confirmed Tuesday.
The department said those infected include 4 children and 3 adults. Nearly 900 residents have received vaccines since Thursday night, officials said.
The vaccine against measles is not recommended during pregnancy or for children younger than 1.
“We haven’t seen cases of new arrivals coming with measles,” the city’s public health Commissioner Dr. Olusimbo Ige said Wednesday. “Measles cases were acquired here. And so, we have been working very hard, taking our responsibility to safeguard the health of the new arrivals seriously.”
The cluster within the city-run shelter highlighted Chicago’s multi-layered struggle to respond to the arrival of nearly 37,000 migrants since 2022 when Texas Gov. Greg Abbott began sending buses to so-called sanctuary cities.
Chicago initially used police stations and airports as officials searched for other temporary shelters. On Tuesday, a city dashboard showed more than 11,000 people remain in city-run shelters.
Providing medical care has been part of that effort; from vaccinations to treatment of conditions developed during exhausting journeys to reach the U.S. border with Mexico.
Many migrants who land in Chicago come from Venezuela where a social, political and economic crisis has pushed millions into poverty. The situation along with doctor and drug shortages has affected the availability and affordability of routine care, as well as trust in medical institutions. Venezuela has reported one of the world’s lowest vaccination rates for children.
Cook County officials opened a clinic to provide immediate care, vaccinations and an entryway into other public health services in 2022.
Alex Normington, a spokesperson for Cook County Health, said providers offer all essential vaccinations there and more than 73,000 have been given against measles, influenza, COVID-19 and other viruses.
Providers also rotate through every city shelter and have expanded their hours as the measles cases arose, Normington said.
But volunteer organizations working with migrants have frequently criticized conditions inside the city’s shelters, particularly following the December death of a five-year-old boy who became ill while staying at the same shelter where the measles cases have been reported.
They argue the cases are the result of the city, county, state and federal government falling short of supporting new arrivals’ health needs.
“This is not the new arrivals’ fault — this is a public health emergency a long time in the making,” Annie Gomberg, a volunteer, said in a statement. “Everyone arriving here should be screened and vaccinated, just like we did at Ellis Island over 100 years ago. Not put in overcrowded shelters to languish.”
___
Associated Press reporter Sophia Tareen in Chicago and medical writer Mike Stobbe in New York contributed.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently dispatched a team to assist in the response to seven confirmed cases of measles at a migrant shelter in Chicago. The outbreak, which was first reported in early September, has raised concerns about the potential spread of the highly contagious virus among vulnerable populations.
Measles is a viral infection that can cause fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic rash. In severe cases, it can lead to complications such as pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death. The virus is spread through respiratory droplets and can remain airborne for up to two hours after an infected person has left the area.
The CDC team deployed to the Chicago migrant shelter is working closely with local health officials to contain the outbreak and prevent further transmission of the virus. Their efforts include conducting contact tracing to identify individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, providing vaccinations to those who are not immune, and implementing infection control measures to limit the spread of the virus within the shelter.
In addition to their on-the-ground response, the CDC team is also working to raise awareness about the importance of vaccination in preventing measles outbreaks. Measles is a vaccine-preventable disease, and the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is highly effective at protecting individuals from infection. However, vaccination rates have been declining in recent years due to misinformation and vaccine hesitancy.
The outbreak at the Chicago migrant shelter serves as a stark reminder of the importance of maintaining high vaccination coverage rates to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. It also highlights the challenges faced by vulnerable populations, such as migrants, who may have limited access to healthcare services and vaccines.
As the CDC team continues their response efforts in Chicago, it is crucial for individuals to stay informed about the symptoms of measles and the importance of vaccination. By working together to promote vaccination and implement effective public health measures, we can help prevent future outbreaks and protect the health of our communities.