Japan’s Recent Launch: Exploring the Origins of the Universe with Lunar Lander and X-ray Telescope
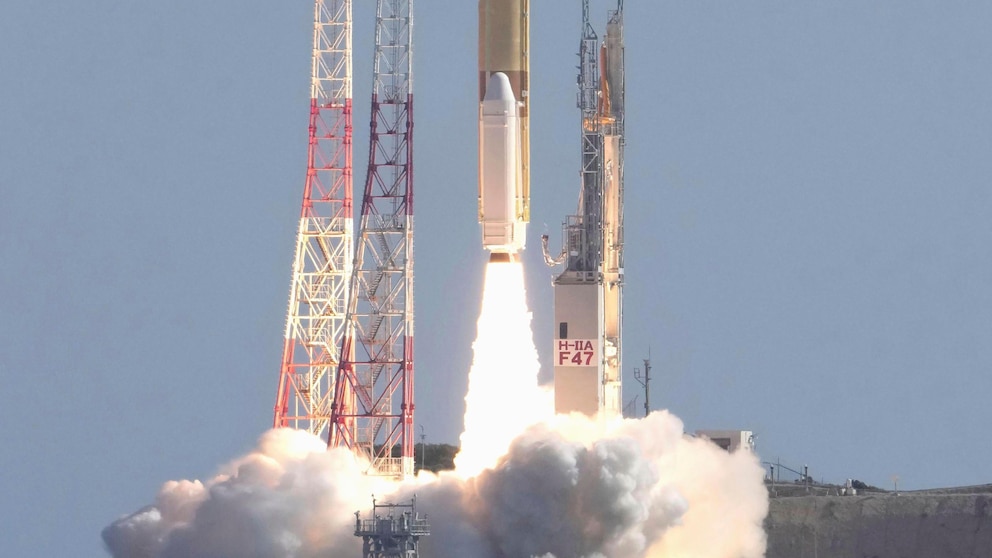
In a significant step towards unraveling the mysteries of the universe, Japan has recently launched a lunar lander and an X-ray telescope. This ambitious mission aims to explore the origins of the universe and shed light on some of the most fundamental questions in astrophysics.
The lunar lander, named Kaguya, was launched by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in collaboration with other international partners. Its primary objective is to study the moon’s surface and its geological features. However, Kaguya also carries instruments that will contribute to our understanding of the universe’s origins.
One of the key instruments aboard Kaguya is the Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR). This radar will be used to investigate the moon’s subsurface structure, providing valuable insights into its geological history. By studying the moon’s composition and how it has evolved over time, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of the early solar system and the processes that led to the formation of planets.
Another significant component of this mission is the X-ray telescope, called X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM). This telescope will be launched into space and will focus on observing X-rays emitted by celestial objects such as black holes, supernovae remnants, and galaxy clusters. By studying these X-rays, scientists can gather crucial information about the high-energy processes occurring in these cosmic phenomena.
The XRISM telescope is equipped with advanced imaging and spectroscopic capabilities, allowing scientists to analyze the X-rays in detail. This will help them understand the physical properties of these objects, such as their temperature, density, and chemical composition. By studying these characteristics, scientists can gain insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies, as well as the role played by black holes in shaping the universe.
The combination of the lunar lander and the X-ray telescope provides a unique opportunity for scientists to explore the origins of the universe from two different perspectives. While the lunar lander focuses on studying the moon’s geological history, the X-ray telescope will provide insights into the cosmic processes occurring in distant celestial objects.
This mission holds great promise for advancing our understanding of the universe’s origins. By studying the moon’s geological features and the X-rays emitted by celestial objects, scientists can piece together the puzzle of how our universe came into existence and evolved over billions of years.
Furthermore, this mission also highlights Japan’s commitment to space exploration and scientific research. Japan has made significant contributions to space science in recent years, with successful missions like Hayabusa2, which collected samples from an asteroid, and Akatsuki, which is studying the atmosphere of Venus. The launch of Kaguya and XRISM further solidifies Japan’s position as a leading player in space exploration.
In conclusion, Japan’s recent launch of the lunar lander Kaguya and the X-ray telescope XRISM represents a significant milestone in our quest to understand the origins of the universe. By studying the moon’s geological history and observing X-rays emitted by celestial objects, scientists hope to uncover the secrets of how our universe came to be. This mission not only holds immense scientific value but also showcases Japan’s prowess in space exploration and its commitment to pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.