Title: Report Reveals an 18% Surge in Global Measles Cases in 2022 Due to Low Vaccination Rates
Introduction
Measles, a highly contagious viral disease, has made a concerning resurgence worldwide in 2022. A recent report has revealed an alarming 18% surge in global measles cases, primarily attributed to low vaccination rates. This article aims to shed light on the causes behind this surge, the consequences of low vaccination rates, and the importance of immunization in preventing the spread of measles.
The Global Measles Surge
According to the report, the global measles cases in 2022 have reached unprecedented levels, with an 18% increase compared to the previous year. This surge has affected countries across all continents, including both developed and developing nations. The World Health Organization (WHO) has expressed deep concern over this rise, as measles is a preventable disease through vaccination.
Causes of Low Vaccination Rates
Several factors contribute to the low vaccination rates that have fueled the measles surge. Misinformation and vaccine hesitancy have played a significant role in discouraging people from getting vaccinated. False claims linking vaccines to autism or other adverse effects have spread through social media platforms, leading to a decline in public trust in vaccines.
Additionally, inadequate access to healthcare services and vaccines in certain regions, particularly in low-income countries, has hindered vaccination efforts. Conflict zones and areas with weak healthcare infrastructure face challenges in delivering vaccines to vulnerable populations, leaving them susceptible to measles outbreaks.
Consequences of Low Vaccination Rates
The consequences of low vaccination rates are dire. Measles is highly contagious and can spread rapidly among unvaccinated individuals. Complications from measles can be severe, including pneumonia, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and even death. Infants, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable.
Moreover, the resurgence of measles strains healthcare systems, diverting resources and personnel away from other critical health issues. Outbreaks strain hospital capacities, leading to increased healthcare costs and a burden on already limited resources.
The Importance of Immunization
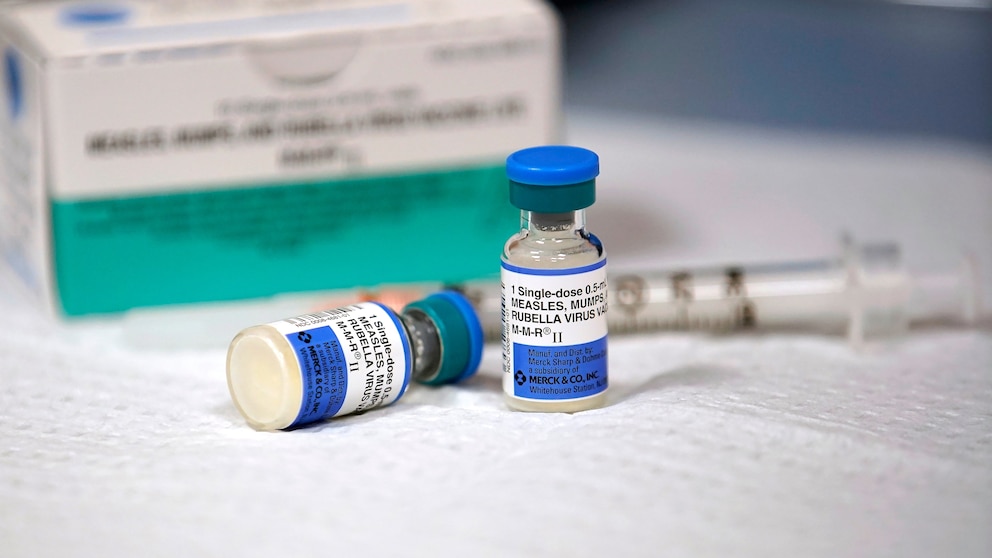
Immunization is the most effective way to prevent measles and its devastating consequences. The measles vaccine, typically administered as part of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, provides long-lasting immunity against the virus. Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to herd immunity, reducing the overall transmission of the disease within a population.
To combat the surge in measles cases, it is crucial to address vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. Governments and healthcare organizations must invest in public awareness campaigns to educate communities about the safety and efficacy of vaccines. Healthcare providers should engage with hesitant individuals, addressing their concerns and providing accurate information.
Furthermore, efforts to improve access to vaccines must be prioritized, especially in underserved areas. Governments and international organizations should collaborate to strengthen healthcare infrastructure, ensuring that vaccines reach all communities, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status.
Conclusion
The 18% surge in global measles cases in 2022 due to low vaccination rates is a cause for concern. Measles is a highly contagious disease that can have severe consequences, particularly for vulnerable populations. To combat this surge, it is imperative to address vaccine hesitancy, misinformation, and improve access to vaccines. By prioritizing immunization efforts globally, we can protect individuals, prevent outbreaks, and work towards eliminating measles as a public health threat.