The Drifting of One of the World’s Largest Icebergs Beyond Antarctic Waters
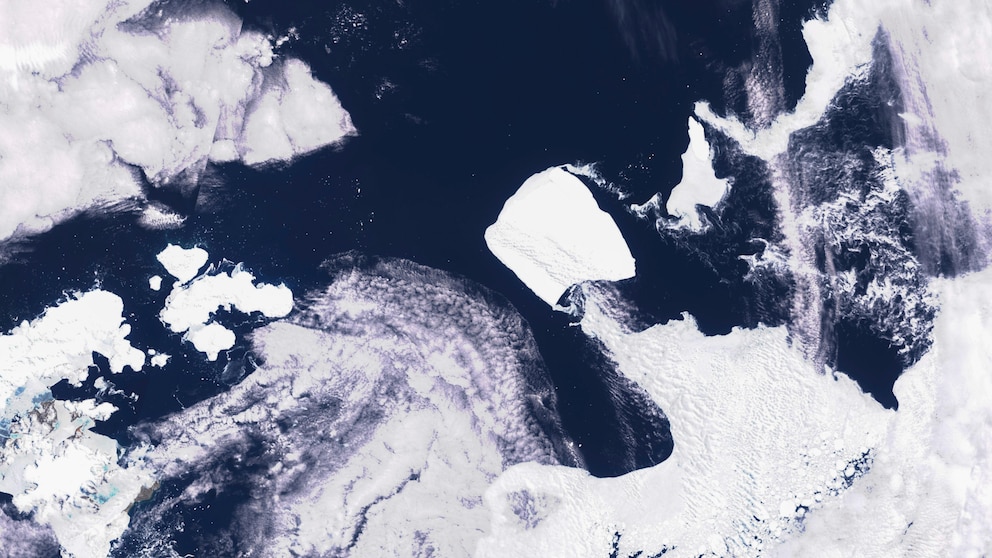
In a significant event that has captured the attention of scientists and the public alike, one of the world’s largest icebergs has recently drifted beyond Antarctic waters. This monumental occurrence raises concerns about the impact of climate change on the stability of polar ice shelves and the potential consequences for global sea levels.
The iceberg, known as A-76, was first detected by the European Space Agency’s Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission in May 2021. With an area of approximately 4,320 square kilometers (1,670 square miles), it is larger than the state of Rhode Island and ranks among the largest icebergs ever recorded. A-76 broke off from the Ronne Ice Shelf, located in the Weddell Sea, which is part of the larger Antarctic Ice Sheet.
The drifting of A-76 beyond Antarctic waters is a stark reminder of the ongoing changes occurring in the polar regions due to climate change. Rising temperatures have accelerated the melting of ice shelves, leading to an increased frequency of iceberg calving events. While iceberg calving is a natural process, the size and frequency of these events have raised concerns among scientists.
The detachment of such a massive iceberg has several potential consequences. Firstly, it can disrupt ocean currents and marine ecosystems. As icebergs drift, they can alter the flow of ocean currents, impacting nutrient distribution and disrupting the habitats of marine organisms. This can have far-reaching effects on the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, affecting both local and global biodiversity.
Secondly, the drifting of large icebergs can contribute to rising sea levels. While icebergs are already floating in water and their melting does not directly contribute to sea-level rise, their detachment from ice shelves allows glaciers and ice sheets to flow more rapidly into the ocean. This phenomenon, known as “ice shelf collapse,” can lead to increased sea-level rise over time.
The drifting of A-76 also highlights the need for continued monitoring and research in the polar regions. Scientists rely on satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies to track the movement and behavior of icebergs. This data helps improve our understanding of ice dynamics, which is crucial for predicting future changes in ice shelves and their impact on global sea levels.
Furthermore, this event serves as a reminder of the urgent need to address climate change. The warming of our planet is directly linked to the destabilization of polar ice shelves and the subsequent release of massive icebergs. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting sustainable practices, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and preserve the delicate balance of our planet’s polar regions.
In conclusion, the drifting of one of the world’s largest icebergs, A-76, beyond Antarctic waters is a significant event that highlights the ongoing changes occurring in the polar regions due to climate change. This event raises concerns about the disruption of marine ecosystems, potential sea-level rise, and underscores the importance of continued research and action to address climate change. It serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need to protect our planet’s fragile ice shelves and mitigate the impacts of global warming.