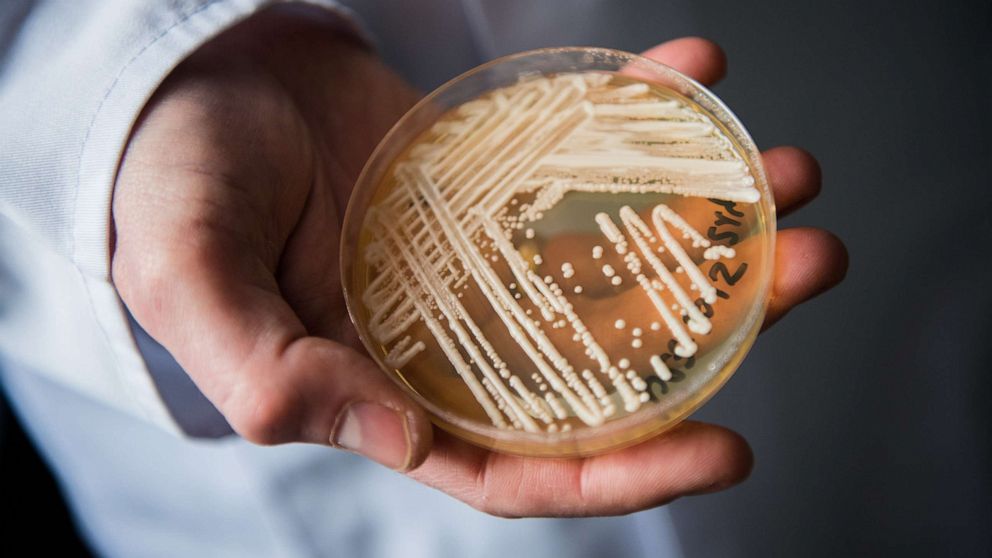
Health departments across the world are increasingly concerned about the spread of a potentially fatal fungus known as Candida auris. This fungus has been identified in more than 30 countries and is known to cause serious infections that are difficult to treat. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind health departments’ concerns about the spread of this fungus.
Firstly, Candida auris is a multidrug-resistant fungus, which means that it is resistant to multiple antifungal drugs that are commonly used to treat fungal infections. This makes it difficult to treat and can result in prolonged hospitalization, increased healthcare costs, and even death. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has classified Candida auris as an urgent threat to public health.
Secondly, Candida auris is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in healthcare settings. It can survive on surfaces for weeks and can be easily transmitted from person to person through contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment. This makes it difficult to control and contain outbreaks, especially in hospitals and long-term care facilities where patients are already vulnerable to infections.
Thirdly, Candida auris is often misidentified or undetected, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. This is because it can be easily mistaken for other types of fungi or bacteria, and standard laboratory tests may not be able to detect it. This can result in the spread of the fungus and increased risk of complications.
Fourthly, Candida auris is often associated with underlying health conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and immunosuppression. This means that people with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of developing infections caused by this fungus. In addition, people who have been hospitalized or have received antibiotics or antifungal medications are also at an increased risk of developing infections caused by Candida auris.
Finally, there is limited knowledge about the origin and transmission of Candida auris. It is believed to have emerged relatively recently and its exact origin is still unknown. This makes it difficult to develop effective prevention and control strategies.
In conclusion, the spread of Candida auris is a major concern for health departments around the world. Its multidrug-resistant nature, high contagiousness, difficulty in detection, association with underlying health conditions, and limited knowledge about its origin and transmission make it a serious threat to public health. It is important for healthcare providers, policymakers, and the public to be aware of this fungus and take necessary precautions to prevent its spread.